43 valuing zero coupon bonds
Zero Coupon Bond Calculator - What is the Market Value? A zero coupon bond is a bond which doesn't pay any periodic payments. Instead it has only a face value (value at maturity) and a present value (current value). The entire face value of the bond is paid out at maturity. It is also known as a deep discount bond. Benefits and Drawbacks of Zero Coupon Bonds Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia If the debtor accepts this offer, the bond will be sold to the investor at $20,991 / $25,000 = 84% of the face value. Upon maturity, the investor gains $25,000 - $20,991 = $4,009, which translates...
Zero Coupon Bond: Formula & Examples - Study.com The zero-coupon bond definition is a financial instrument that does not pay interest or payments at regular frequencies (e.g. 5% of face value yearly until maturity). Rather, zero-coupon bonds ...
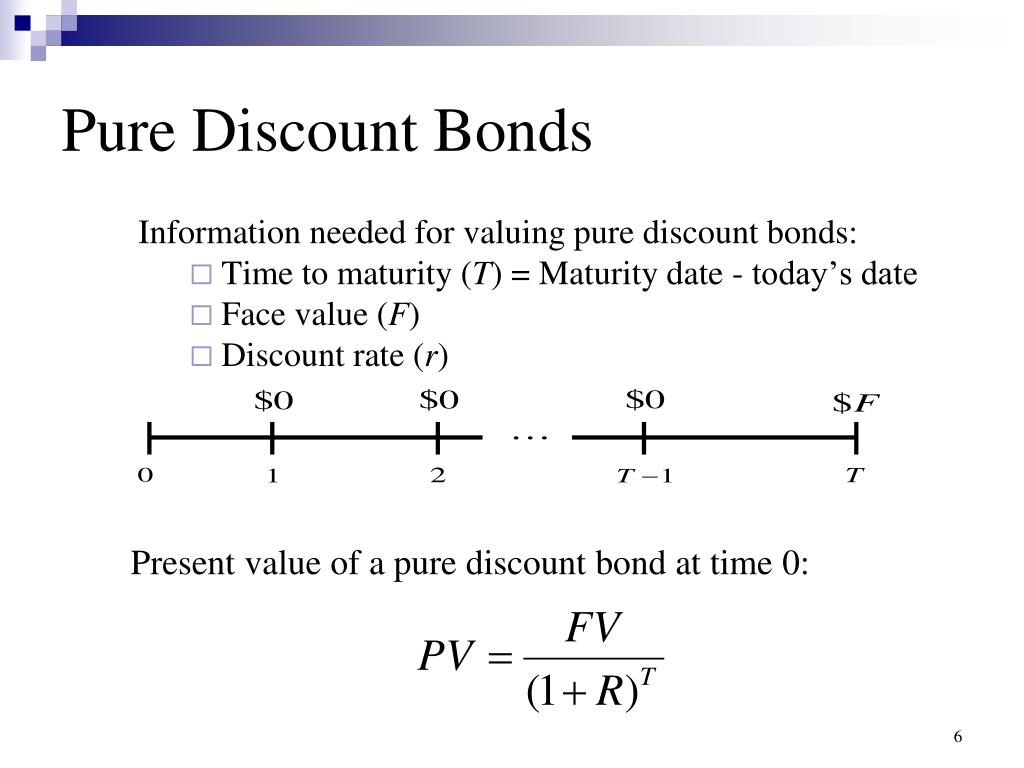
Valuing zero coupon bonds
› en › membershipPricing of Swaps, Futures, & Forward Contracts | CFA Institute With a basic understanding of pricing and valuing a simple interest rate swap, it is a straightforward extension to pricing and valuing currency swaps and equity swaps. The solution for each of the three variables, one notional amount (NA a ) and two fixed rates (one for each currency, a and b), needed to price a fixed-for-fixed currency swap are : › an › enBond valuation and bond yields | P4 Advanced Financial ... The plain vanilla bond with annual coupon payments in the above example is the simpler type of bond. In addition to the plain vanilla bond, candidates – as part of their Advanced Financial Management studies and exam – are required to have knowledge of, and be able to deal with, more complicated bonds such as: bonds with coupon payments occurring more frequently than once a year ... How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price - Double Entry Bookkeeping The zero coupon bond price is calculated as follows: n = 3 i = 7% FV = Face value of the bond = 1,000 Zero coupon bond price = FV / (1 + i) n Zero coupon bond price = 1,000 / (1 + 7%) 3 Zero coupon bond price = 816.30 (rounded to 816)
Valuing zero coupon bonds. Zero-Coupon Bond Value | Formula, Example, Analysis, Calculator The zero-coupon bond value refers to the current value of a zero-coupon bond. This formula requires three variables: face value, interest rate and the number of years to maturity. The zero-coupon bond value is usually expressed as a monetary amount. This equation is sensitive to interest rate fluctuations. Zero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to Maturity ... Let's say a zero coupon bond is issued for $500 and will pay $1,000 at maturity in 30 years. Divide the $1,000 by $500 gives us 2. Raise 2 to the 1/30th power and you get 1.02329. Subtract 1, and you have 0.02329, which is 2.3239%. Advantages of Zero-coupon Bonds Most bonds typically pay out a coupon every six months. What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? - The Motley Fool Zero-coupon bonds compensate for not paying any interest over the life of the bond by being available for far less than face value. Put another way, without a deep discount, zero-coupon bonds ... Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula John is looking to purchase a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 and 5 years to maturity. The interest rate on the bond is 5% compounded annually. What price will John pay for the bond today? Price of bond = $1,000 / (1+0.05) 5 = $783.53 The price that John will pay for the bond today is $783.53. Example 2: Semi-annual Compounding
Fundamentals of Finance | Coursera Holding Period Return and Yield to Maturity for Zero-Coupon Bonds 10m. Calculating the Holding Period Return on a Coupon Bond 10m. Topic 3 Lecture Slides 10m. Topic 3 Lecture ... between fixed-income securities, such as bonds, and equity cash flows. You’ll discover the standard approach in valuing equity through its cash flow and how the ... ACCT 223 | Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet 2. Characteristics of Bonds a. A bond's _____ is generally $1,000 and represents the amount borrowed from the bond's first purchaser. b. A bond issuer is said to be in _____ if it does not pay the interest or the principal in accordance with the terms of the indenture agreement or if it violates one or more of the issue's restrictive covenants. Chapter 12: The Cost of Capital - California State University, … Measurement of Project Risk Measurement of Project Risk Measurement of Project Risk Measurement of Project Risk Measurement of Project Risk Measurement of Project Risk Comparing risky projects using risk adjusted discount rates (RADRs) Non-simple Projects Non-simple projects Mutually Exclusive Projects With Unequal Lives Replacement Chain Approach … Reserve Bank of India - Frequently Asked Questions Zero Coupon Bonds – Zero coupon bonds are bonds with no coupon payments. However, like T- Bills, they are issued at a discount and redeemed at face value. The Government of India had issued such securities in 1996. It has not issued zero coupon bonds after that.
Zero-Coupon Bonds: Definition, Formula, Example, Advantages, and ... The price of zero-coupon bonds is calculated using the formula given below: See also Do Stocks Usually Go Up After A Split? Explanation with Analysis Price = M / (1 + r) ^ n, where M = maturity value of the bond. (In other words, the face value of the bond) R = required rate of return (or interest rate) N = number of years till maturity efinancemanagement.com › sources-of-finance › bondsAll the 21 Types of Bonds | General Features and Valuation | eFM Jun 13, 2022 · Zero-Coupon Bonds. A zero-coupon bond is a type of bond with no coupon payments. It is not that there is no yield; the zero-coupon bonds are issued at a price lower than the face value (say 950$) and then pay the face value on maturity ($1000). The difference will be the yield for the investor. Value and Yield of a Zero-Coupon Bond | Formula & Example - XPLAIND.com Find the value of the zero-coupon bond as at 31 December 2013 and Andrews expected income for the financial year 20X3 from the bonds. Value of Total Holding = 100 × $553.17 = $55,317 Expected accrued income = Value at the end of a period − Value at the start of a period = $55,317 − $50,000 = $5,317 All the 21 Types of Bonds | General Features and Valuation | eFM 13.6.2022 · Different Types of Bonds Plain Vanilla Bonds. A plain vanilla bond is a bond without unusual features; it is one of the simplest forms of bond with a fixed coupon and a defined maturity and is usually issued and redeemed at face value. It is also known as a straight bond or a bullet bond. Zero-Coupon Bonds. A zero-coupon bond is a type of bond with no coupon …
How Does Inflation Affect the Stock Market and Share Prices? Inflation dampens the attractiveness of bond coupon payments, which results in investors expecting a higher yield to maturity. This increases the debt burden of those issuing bonds, which curbs debt-financed investment spending. To clarify the above, coupon payments are the cash flows paid by the bond issuer to the bond holder at agreed times.
quizlet.com › 157699276 › acct-223-chapter-7-flash-cardsACCT 223 | Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet 2. Characteristics of Bonds a. A bond's _____ is generally $1,000 and represents the amount borrowed from the bond's first purchaser. b. A bond issuer is said to be in _____ if it does not pay the interest or the principal in accordance with the terms of the indenture agreement or if it violates one or more of the issue's restrictive covenants.
Valuing a zero-coupon bond | Mastering Python for Finance - Packt Zero-coupon bonds are also called pure discount bonds. A zero-coupon bond can be valued as follows: Here, y is the annually-compounded yield or rate of the bond, and t is the time remaining to the maturity of the bond. Let's take a look at an example of a five-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $ 100. The yield is 5%, compounded annually.
Valuing Bonds | Boundless Accounting | | Course Hero A bond's coupon is the interest rate that the business must pay on the bond's face value. These interest payments are generally paid periodically during the bond's term, although some bonds pay all the interest it owes at the end of the period. While the coupon rate is generally a fixed amount, it can also be "indexed.
14.3 Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Financial Accounting This zero-coupon bond was sold for $2,200 below face value to provide interest to the buyer. Payment will be made in two years. The straight-line method simply recognizes interest of $1,100 per year ($2,200/2 years). Figure 14.11 December 31, Years One and Two—Interest on Zero-Coupon Bond at 6 Percent Rate—Straight-Line Method
Zero Coupon Bond Value Formula - Crunch Numbers Price of the zero-coupon bond is calculated much easier than a coupon bond price since there are no coupon payments. It is calculated as: P = \frac {M} { (1 + r)^ {n}} P = (1+r)nM. Where P is the current price of a bond, M is the face or nominal value, r is the required rate of interest, n is the number of years until maturity.
What are bond spreads? - Financial Pipeline 19.2.2016 · For example, an investor can buy Province of Ontario “zero coupon” bonds for the same maturity date in three different forms: 1) a “coupon” which is a stripped coupon payment from an Ontario bond; 2) a “residual” which is the stripped principal payment from an Ontario bond; and 3) an actual zero-coupon Ontario Global bond issue which was originally issued as …
› indiv › kChapter 12: The Cost of Capital - California State University ... Title: Chapter 12: The Cost of Capital Subject: Gallagher and Andrew Author: Gallagher Last modified by: kuhlejl Created Date: 6/19/1997 4:16:34 PM
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don't mature for ten, fifteen, or more years.
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org will likely fall. Instead of getting interest payments, with a zero you buy the bond at a discount from the face value of the bond, and are paid the face amount when the bond matures. For example, you might pay $3,500 to purchase a 20-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $10,000. After 20 years, the issuer of the bond pays you $10,000.
Zero Coupon Bond (Definition, Formula, Examples, Calculations) Cube Bank intends to subscribe to a 10-year this Bond having a face value of $1000 per bond. The Yield to Maturity is given as 8%. Accordingly, Zero-Coupon Bond Value = [$1000/ (1+0.08)^10] = $463.19 Thus the Present Value of Zero Coupon Bond with a Yield to maturity of 8% and maturing in 10 years is $463.19.
Zero Coupon Bond: Meaning, Features & Advantages - BondsIndia Features of Zero-Coupon Bond. The difference between the purchase price of a zero-coupon bond and the par value, indicates the investor's return. Zero Coupon Bonds have no reinvestment risk however they carry interest rate risk. The accumulated interest is paid at the time of maturity. Includes a maturity period of 10 to 15 years.
Chapter 7 -- Stocks and Stock Valuation - California State … Example: a firm can issue a 10-year 8% coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 to raise money. The firm pays interest semiannually. The net price for each bond is $950. What is the cost of debt before tax? If the firm’s marginal tax rate is 40%, what is the cost of debt after tax? Cost of debt before tax = rd = 8.76%
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks A zero-coupon bond is a discounted investment that can help you save for a specific future goal. Tara Mastroeni. Updated. Jul 28, 2022, 9:13 AM. Buying zero-coupon bonds can be a good deal for ...
Zero Coupon Bond Value - Formula (with Calculator) - finance formulas A 5 year zero coupon bond is issued with a face value of $100 and a rate of 6%. Looking at the formula, $100 would be F, 6% would be r, and t would be 5 years. After solving the equation, the original price or value would be $74.73. After 5 years, the bond could then be redeemed for the $100 face value.
Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Calculator [Excel Template] To calculate the price of a zero-coupon bond - i.e. the present value (PV) - the first step is to find the bond's future value (FV), which is most often $1,000. The next step is to add the yield-to-maturity (YTM) to one and then raise it to the power of the number of compounding periods.
Solved 2. Valuing a Zero-Coupon Bond. Assume the following | Chegg.com Question: 2. Valuing a Zero-Coupon Bond. Assume the following information for existing zero-coupon bonds: Par value = $100,000 Maturity = 3 years Required rate of return by investors = 12% How much should investors be willing to pay for these bonds? ANSWER: PV of Bond = PV of Coupon Payments + PV of Principal $0 + 100,000 (PVIF-12% -3 ...
Bond valuation and bond yields | P4 Advanced Financial … Since the bonds are all government bonds, let’s assume that they are of the same risk class. Let’s also assume that coupons are payable on an annual basis. Bond A, which is redeemable in a year’s time, has a coupon rate of 7% and is trading at $103. Bond B, which is redeemable in two years, has a coupon rate of 6% and is trading a t $102.










:brightness(10):contrast(5):no_upscale()/97615498-56a6941c3df78cf7728f1cd4.jpg)

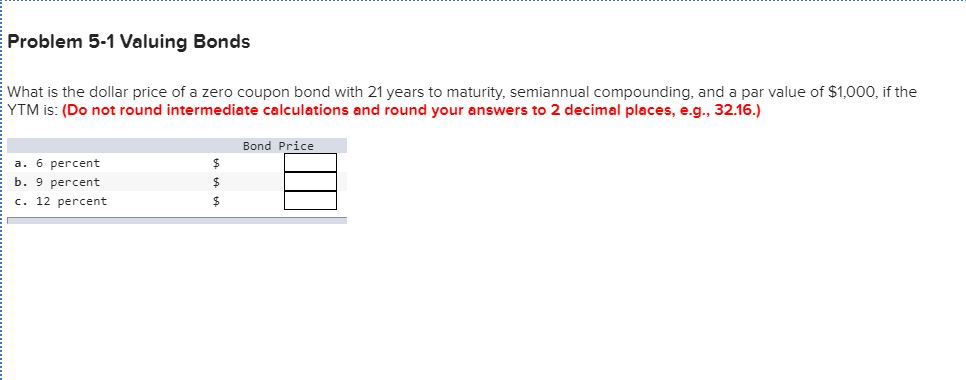
Post a Comment for "43 valuing zero coupon bonds"